How to Perform Bobcat Loader Lift & Tilt Calibration by Actuator Test
Chinaobd2 is a leading supplier of all kinds of Car Diagnostic Tool, Truck Diagnostic Tool, OBD2 Code Reader, Car Key Programmer,ECU Chip Tunning,etc. Currently, the top selling product including: VCDS VAG COM Cable, iProg+ Programmer, Scania VCI3
Bobcat Calibration procedures must be followed when replacing hydraulic control valve, actuator, Drive / Drive+Controller, ACS Controller, pump controller, hydrostatic pump, or hydrostatic motor. Failure to calibrate after component replacement may result in error codes, poor performance or reduced life of actuator(s).There are two methods to perform the lift and tilt calibration, one is the Actuator Test and the other is manually. The Actuator Test is performed with the Service PC. The Actuator Test should be used if reduced performance codes are present or when replacing a controller or actuator.The Lift and Tilt Calibration (SJC) is performed by physically moving the joysticks to provide set points to the ACS controller to actuate the lift and tilt valve. The Lift and Tilt Calibration (SJC) should be used if reduced performance codes are present or when replacing a controller or actuator.
BATS 2018 Bobcat Advanced Troubleshooting System Installation Guide
NOTE:The Actuator Test should be used as the preferred method of lift and tilt calibration. The Hydrostatic Pump Calibration (SJC / SCPA) provides set points to the Drive controller to actuate the hydrostatic controller that directs flow to a servo piston.Hydrostatic Pump Calibration (SJC / SCPA) should be performed when a desired travel path cannot be at tained or replacing the hydrostatic pump, hydrostatic motor, or controller. After Performing a Hydrostatic Pump Calibration (SJC / SCPA), Steering Drift Compensation can be used to fine tune the hydrostatic pump control.For more information on Steering Drift Compensation(See STEERING DRIFT COMPENSATION on Page 60-161-1.)NOTE: The Actuator Test calibrates the lift and tilt system therefore no further lift and tilt calibration is required if using this method.
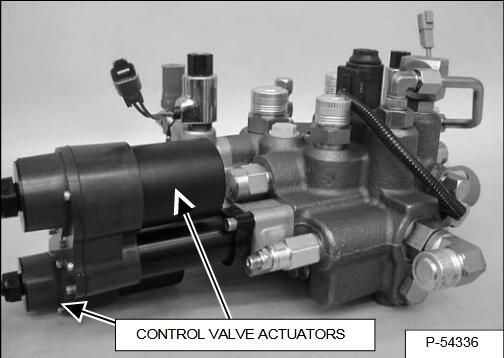
Excessive actuator loading can occur if the actuator and valve spool components are misaligned. Misalignment may reduce spool stroke performance and reduce the life of the actuator.
Connect the Service PC.
If a Service PC is not available
NOTE:Warm the hydraulic oil to room temperature22°C (72°F), stop the engine and clear all active service codes before running the test.
Once the test is initiated, an automatic calibration sequence will start. When calibration is complete, the test will be performed and the results can be viewed on the Service PC monitor.
Actuator Testing (Cont’d)
This test will engage both actuators to fully stroke the spools then allow the centering springs to return the spools to neutral. Next, both actuators are engaged to move the spools just past the neutral points then allow the centering springs to return the spools to neutral.When complete, the Actuator Test will show a pass mode or fail mode. The pass mode indicates that no problems were detected. The fail mode indicates one or a combination of three problems below.
- Actuator slow return to neutral. The spool returns toneutral too slowly.
- Actuator did not fully extend / retract. During the test,the spool was not able to fully stroke in bothdirections.
- Actuator out of neutral. The spool did not return to theneutral window during the test.
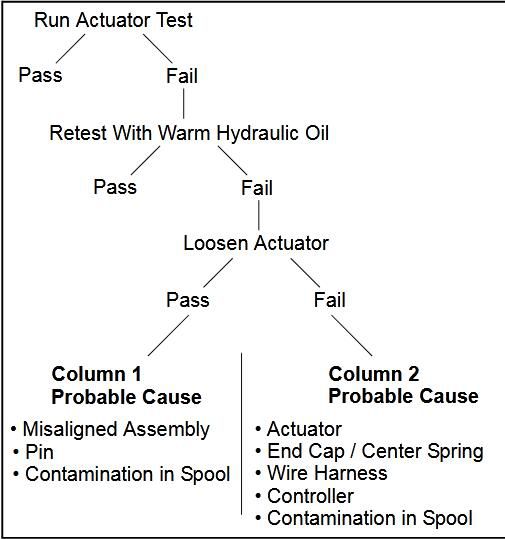
If the initial Actuator Test results in a fail mode due to a slow return to neutral, follow the troubleshooting tree to pinpoint the probable cause.
If the Actuator Test fails after the hydraulic oil is warmed,go to the next step and loosen the bolts that mount the actuator to the control valve. Loosen the bolts just enough so the actuator can be moved slightly up / down or side / side.
Rerun the Actuator Test, if the test passes, check the following probable causes in Column 1. Check the probable causes in the order they are listed. Repairing one cause may be all that is required.Re-run the test to verify.
NOTE: Actuator and spool misalignment. Re-tighten the two bolts evenly, turn the first bolt one turn, then turn the other bolt one turn until both bolts are tight.
If the Actuator Test failed due to a slow return to neutral after checking the probable causes in Column 1,check the following probable causes in Column 2.
- Contamination in the spool.
- The spool end cap may be loose, damaged or thecentering spring may be broken. Inspect the end capand the centering spring, replace if necessary.
- The wire harness or connectors may have anintermittent short. Check the connections and wireharnesses.
- The controller may be malfunctioning, replace thecontroller.
- The actuator connectors may be reversed betweenthe lift and tilt actuator. Reverse the connectors andrerun the Actuator Test.
- The actuator may be weak, replace the actuator.
- The spool end cap may be loose, damaged or thecentering spring may be broken. Inspect the end capand the centering spring, replace if necessary.
- Contamination in the spool.If the initial Actuator Test results in the fail mode actuatorout of neutral, check the following.
- The actuator may be weak, replace the actuator.
- The spool end cap may be loose, damaged or thecentering spring may be broken. Inspect the end capand the centering spring, replace if necessary.
- Contamination in the spool.
This article tech Supported by China OBD2,

No comments:
Post a Comment